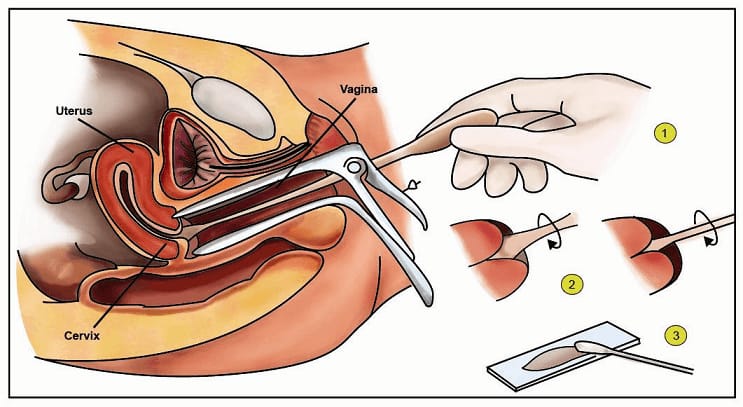
Cervical Cancer Screening
In India, cervical cancer contributes to approximately 6–29% of all cancers in women. All women should begin cervical cancer screening at age 21 using the following methods:
- Age 21-29: Pap testing done every 3 years. HPV testing is used only to follow up abnormal Pap results.
- Age 30-65: Pap testing and HPV test done every 5 years. Alternatively, a woman could have a Pap test alone every 3 years.
- Over age 65: Women who have had regular cervical cancer testing in the past 10 years with normal results no longer need to be tested. Women with a history of a serious cervical pre-cancer should continue to be tested for at least 20 years.
Women who have had their uterus & cervix removed for reasons not related to cervical cancer and have no history of cervical cancer or pre-cancer do not need testing. If the hysterectomy was done as treatment for pre-cancer the above guidelines should be followed or you should follow the guidelines that your doctor gives you.
Women who have had the HPV vaccination should still have Pap testing per the above guidelines.
HPV vaccination is for primary prevention (serotype-specific with limited cross-protection) of carcinoma cervix. There is no risk of getting an HPV infection from the vaccine as the vaccine does not contain live virus.
The CDC and the American Academy of Pediatrics recommend that the vaccine be given routinely to girls at age 11 to 12 years old, although doctors may choose to vaccinate girls as young as 9. The CDC also recommends the vaccine for women age 13 to 26 who did not receive the vaccine at an earlier age.
FDA expands use of cervical cancer vaccine up to age 45.
The main benefit of the vaccine is protection from cervical cancer. Two HPV vaccines are currently on the market: Gardasil and Cervarix.
Children who start the vaccine series before their 15th birthday need only two doses to be fully protected. People who start the series at age 15 or older and people who have certain conditions that weaken the immune system need three doses to be fully protected.
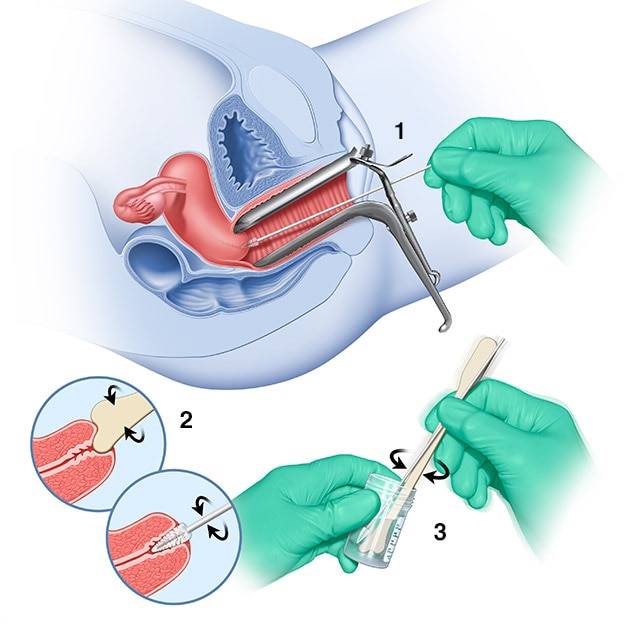
Why is the HPV vaccine important?
Genital HPV is a common virus that is passed from one person to another through direct skin-to-skin contact during sexual activity. Most sexually active people will get HPV at some time in their lives, though most will never even know it. HPV infection is most common in people in their late teens and early 20s. There are about 40 types of HPV that can infect the genital areas of men and women. Most HPV types cause no symptoms and go away on their own. But some types can cause cervical cancer in women and other less common cancers — like cancers of the anus, penis, vagina, and vulva and oropharynx. Other types of HPV can cause warts in the genital areas of men and women, called genital warts. Genital warts are not life-threatening.
HPV vaccination is recommended for 11 and 12 year-old girls. It is also recommended for girls and women age 13 through 26 years of age who have not yet been vaccinated or completed the vaccine series; HPV vaccine can also be given to girls beginning at age 9 years. CDC recommends 11 to 12 year olds get two doses of HPV vaccine to protect against cancers caused by HPV.
Pregnant woman should not get any doses of the HPV vaccine until her pregnancy is completed.
Gardasil 9 is an HPV vaccine approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and can be used for both girls and boys.
Cervarix vaccine is designed to prevent infection from HPV types 16 and 18.
OPD Timings
Dr. Mandar R Gadgil
| Mon – Fri | - | 4:30 PM - 7:30 PM w.e.f. 27th August 2022 |
| Saturday | - | 10:00 AM - 11:30 AM |
OPD Timings
Dr. Maithilee Gadgil
| MON – SAT | - | 10:00 AM - 12:30 PM |
| MON – FRI | - | 4:30 PM - 07:00 PM w.e.f. 27th August 2022 |
Any Question Or Query
Feel free to ask for your any Question or Query /
Book An Appointment
Appointment
To book appointment call us on